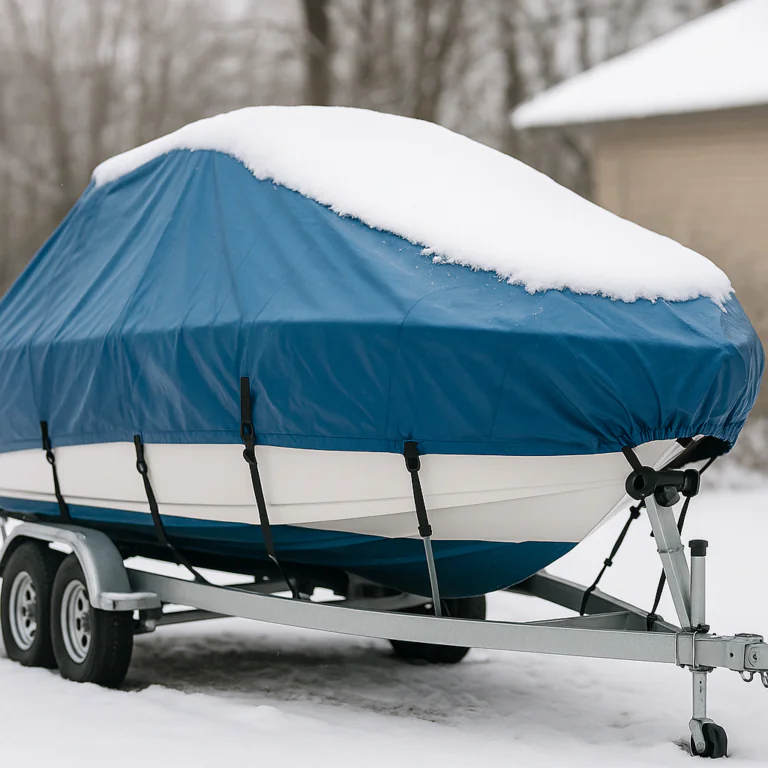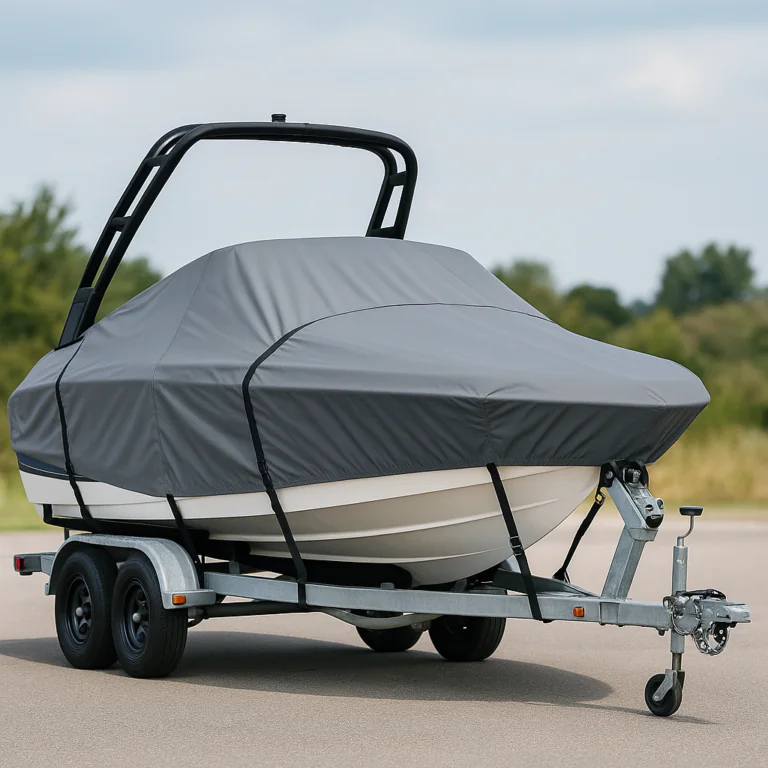
Boat Covers 17-19ft Guide: Fit, Fabric & Maintenance
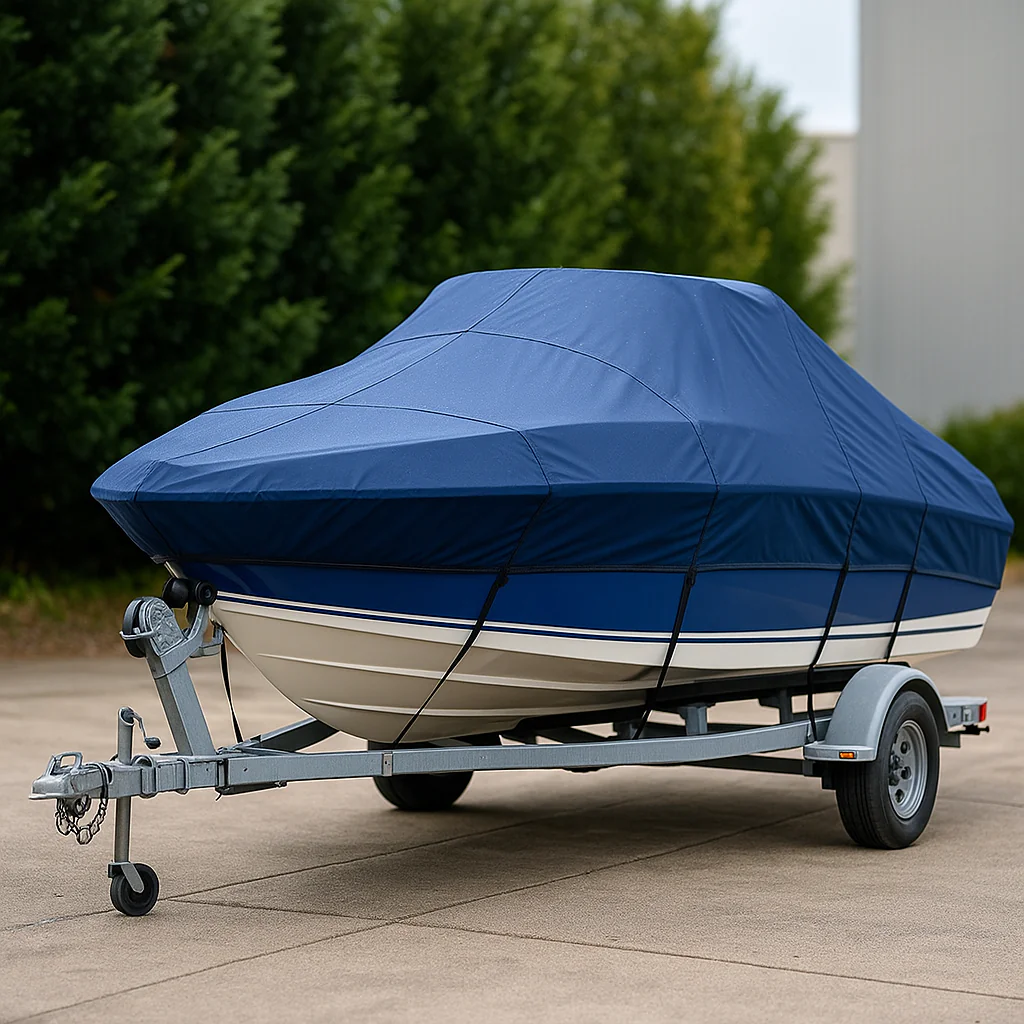

Best Boat Covers 17-19ft: Fit, Fabric & Buying Guide
boat covers 17-19ft are the single most important accessory you can buy to protect a trailerable or moored boat of that size, and choosing the right one starts with exact measuring and a clear plan. This guide walks you through how to measure, which materials matter, and how to match cover type to use so you avoid common mistakes and get a cover that lasts. Early in your process consult the official safety guidance from the U.S. Coast Guard for boater best practices: USCG boating guidance
How to choose the right boat cover 17-19ft
Choosing a cover for boat covers 17-19ft means thinking about three things at once: the boat shape, how you use the boat, and the fit system the cover offers. Start with a checklist and clear measurements so the cover doesn’t end up too short or too loose. If you need a step-by-step measuring resource, see this measuring guide for exact LOA and beam tips.
Measuring your boat correctly (length, beam, console, accessories)
Accurate measurement avoids one of the most common errors: buying a cover that fits hull length but not overall length when consoles, rails, or swim platforms are included. Use this measurement checklist and process.
- Measure overall length (LOA): tape from the furthest forward point (bow rail if present) to the furthest aft point (swim platform, motor mount).
- Record beam: the widest point of the hull plus any fixed rails.
- Measure height: highest point with windshield, console or bimini up, then again with bimini down if removable.
- Note hardware: anchors, trolling motors, rails, and ski poles that extend out from the hull.
- Photograph both sides and bow/stern—sellers appreciate photos when recommending semi‑custom or custom options.
Common mistakes include measuring hull length only, or forgetting removable accessories. For a quick decision flow: use-case → hull type → fit type. If you trailer regularly or have a tower, lean toward semi‑custom or custom fits.
Matching cover type to hull: V‑Hull, Bass, Bowrider, Tri‑Hull, Jet
Hull shape determines where the cover must tighten and where reinforcements are needed. A V‑Hull needs a snug keel line; a bass boat often has a raised casting deck and trolling motor that require strap routing or removable panels. Bowriders have rails and swim platforms that make universal covers risky unless they’re semi‑custom. Jet boats have intake and prop considerations and often need additional cutouts or protective pads. Always communicate hull type to the seller and confirm any reinforcement around outdrives or intakes.
- V‑Hull: prioritize centerline fit and keel straps.
- Bass: note trolling motor, livewell covers, and console height.
- Bowrider: choose semi‑custom to clear rails and platforms.
- Tri‑Hull: wide beam at midship requires wider coverage across straps.
- Jet: protect intakes and prop housings; avoid fabric rubbing on intakes.
Custom vs semi‑custom vs universal: pros and cons
Deciding between custom, semi‑custom, and universal covers is a cost vs fit tradeoff. Custom covers are tailored to your exact boat and accessories; they cost more but reduce wear from flapping and pooling. Semi‑custom (model‑specific) options strike a middle ground for common hulls and popular accessory layouts. Universal covers are cheapest but often underperform in high wind, trailer, or winter snow situations. If you plan to trailer frequently, prioritize reinforced tie points and steel ratchets over the lowest price.
- Custom: best fit, best protection, higher cost.
- Semi‑custom: good balance for common models and towers.
- Universal: economical, lowest protection for unique setups.
Choosing by intended use: storage, mooring, and trailering
Match the cover purpose to features. For mooring, you need smart ventilation, reinforced grommets for tie‑downs, and strong UV resistance. For trailering, choose covers with reinforced straps, lockable grommets, and anti‑flap systems. For long‑term storage, breathable fabrics and taped seams prevent mildew. If you have mixed use, select a heavy‑duty trailering cover with vents and protective pads so it doubles for mooring and storage.
Tip: If you trailer often, don’t use a mooring‑only cover. Look for reinforced straps and ratchet systems designed for highway speeds.
Materials, ratings and construction that matter
Understanding materials is central to choosing the right boat covers 17-19ft. The fabric denier, coating type, seam construction, and reinforcement strategy determine real‑world performance. The goal is to match fabric weight to your use: light and breathable for indoor or seasonal storage, heavier and highly reinforced for trailering and winter exposure.
Fabric types and denier explained (210D, 600D, 1200D, polyester, vinyl)
Denier measures yarn thickness and gives a sense of tear resistance. A 210D fabric is lightweight and works for covers stored indoors or used for short seasonal protection. 600D is a solid all‑around choice for mooring and occasional trailering. 1200D and above (including marine‑grade 900D variants) deliver strong tear resistance and longevity for heavy trailering or northern winter use. Polyester with a PU coating balances strength and UV stability. Vinyl is fully waterproof but heavier and less breathable, so it’s best for high‑exposure storage where ventilation can be managed.
- 210D: light, breathable, indoor/use‑limited.
- 600D: balanced protection for mooring and storage.
- 900–1200D: heavy-duty trailering and winter protection.
Seams, coatings, and waterproof ratings (PU, PVC, Teflon)
Seam quality matters as much as fabric. Taped seams and double stitching reduce leak points. Coatings like PU (polyurethane) provide water resistance while retaining some breathability. PVC and vinyl coatings are more waterproof but trap moisture unless vents are used. Teflon or durable water‑repellent finishes help water bead and run off but don’t replace seam sealing.
Reinforcements, hardware and fit features (grommets, straps, hems)
Look for reinforced bow panels, metal grommets with backing, and strong strap attachment points. Elastic hems help retain fit but aren’t a substitute for ratchets or buckles when trailering. Grommets should be spaced for proper strap routing, and stress points should have additional fabric layers. Check buckle quality and test for corrosion resistance if you store near saltwater.
Ventilation, mildew control and UV protection
Good covers balance waterproofing and breathability. Vents placed low and high promote airflow and prevent condensation. Choose fabrics with UV stabilizers and consider light-colored covers for intense sun. Overlooking ventilation leads to mildew—even on waterproof fabrics—so always plan vent count based on storage duration and climate.
Compare features: what to prioritize for longevity and safety
When comparing boat covers 17-19ft, prioritize features that address your top risks: wind, snow, UV, and trapped moisture. Longevity is a cost per year equation: a slightly higher upfront cost for higher denier and better seams often pays off in longer service life and lower replacement frequency.
Durability vs breathability: balancing tradeoffs
Durability and breathability often pull in opposite directions. Heavy vinyl resists punctures and water but can trap moisture. Lighter breathable fabrics prevent mildew but may wear sooner under road vibration. Match fabric type to primary use and local climate: in humid climates prioritize vents; in snowy regions prioritize strength and support so the cover won’t sag under load.
Snow, wind and trailering performance — real world tests
Real owners report that support poles, reinforced straps, and ratchet systems are the difference between a cover that survives a winter and one that tears. Use support poles at low points to prevent water pooling. Inspect strap routing before highway travel and add chafe guards at contact points on the trailer to prevent fabric wear.
Security, anti‑chafe and anti‑flap solutions
Look for anti‑flap straps, lockable grommets for quick security, and reinforced hem bands. Chafe guards where the cover meets metal or tie‑down points extend fabric life. Always test buckle tension on the ground before towing to ensure no fabric stress points develop on the first trip.
- Inspect straps for webbing quality and stitching.
- Check grommets for reinforced backing plates.
- Install chafe guards where straps cross trailer metal.
Warranty, returns and expected lifespan comparisons
Warranties indicate manufacturer confidence but read exclusions carefully. Expected lifespan depends on exposure and care—properly maintained heavy‑duty covers can last 5–10 years. For additional peace of mind review the manufacturer warranty terms and procedures for claims and repairs before purchase. If warranty activation or registration is required, keep proof of purchase handy.
Buying, installing and maintaining your 17-19ft cover
Buying the right cover is only part of the process. Proper installation and maintenance determine whether your boat covers 17-19ft will protect the vessel through seasons. Before you buy, photograph the boat, note accessories, and confirm return policies and warranty terms with the seller. For product fit and features, review the manufacturer product page to confirm included straps and vents: product page
Step‑by‑step installation for storage and safe trailering
Installation differs for storage vs trailering. For trailering, route straps under trailer frame and use ratchets when provided. For storage, aim for a snug fit with vents and support poles to create a runoff slope.
- Place cover over the boat starting at the bow and smooth aft.
- Secure primary straps at reinforced grommets near bow and stern.
- Route secondary straps under the trailer frame to prevent lift.
- Tighten ratchets evenly; avoid over‑tightening elastic hems.
- Install support poles if storing in winter or where heavy rain can pool.
- Do a walkaround to ensure no straps rub sharp edges—add chafe guards if needed.
Cleaning, reproofing and seasonal maintenance checklist
Wash covers with mild soap and water, rinse well, and let dry fully before storing. Reapply DWR or reproofing treatment if water no longer beads. Inspect seams and hardware quarterly and after storms. Never store a damp cover folded tight—mildew follows. If you want a primer on ventilation and moisture control, see this ventilation guide.
- Quarterly inspection of seams and straps.
- Wash and dry before long storage.
- Reproof every 12–18 months, or as needed.
Simple repairs and when to replace your cover
Small tears can be patched with adhesive patches and seam tape. Replace buckles and grommets if corroded. Replace the cover when multiple seams fail, when the fabric has extensive thinning, or when ventilation and waterproofing are irretrievable with reproofing.
Choosing the right seller: shopping tips and red flags
Buy from sellers who publish clear sizing charts, have a transparent return policy, and provide warranty registration. Red flags include vague fit descriptions, hidden restocking fees, and photos that hide seam detail. Before buying, verify seller credibility and warranty procedures at their official policy pages such as warranty details.
Recommended specs for common 17-19ft boat types
For each common 17–19 ft boat type the recommended minimum specs vary. Use these quick spec checklists to match fabric and construction to your needs and climate.
Bass and V‑Hull fishing boats — recommended minimum specs
Minimum spec: 600D polyester with taped seams, 4+ reinforced straps, and vents. Add a removable panel for trolling motors and a reinforced bow pad if the boat has a raised casting deck. In cold climates select higher denier or additional support poles for snow load.
- Denier: 600D minimum; 900D recommended for winter.
- Seams: taped and double stitched.
- Straps: 4+ reinforced tie points.
Bowriders and runabouts — fit and protection priorities
Bowriders need semi‑custom fits to clear rails and swim platforms. Prioritize coverage for bow rails and transom hardware, and select covers with cutouts or removable panels for ladders and platforms.
Tri‑hull and jet boats — special considerations (outdrives, intakes)
Tri‑hulls are wider midship; choose covers with greater beam allowance. Jet boats need extra protection for intakes and lower unit areas—use additional padding and avoid fabric contact with intakes to prevent abrasion.
Trailer considerations: tie‑downs, support points and legal tips
Secure straps under the trailer and use chafe guards at metal contact areas. Legal tips: ensure nothing extends beyond allowed overhang without proper lighting or flags when towing. Before traveling, check local weather conditions and marine forecasts at the National Weather Service for wind and frost warnings: NWS forecasts and consider NOAA marine alerts at NOAA.
Conclusion
In short, the best boat covers 17-19ft result from a disciplined process: measure thoroughly, choose the right material and seam construction, match the fit to your hull and use, and maintain the cover seasonally. Your highest impact actions are simple: take accurate photos and measurements before ordering, prioritize taped seams and reinforced tie points for trailering, and keep vents and fabric treatments up to date. Final purchase day checklist: measure, confirm spec sheet, verify warranty and returns, and photograph the boat for seller reference. Done right, a quality cover protects your investment and keeps you heading to the water with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between 300D and 600D boat cover?
The main difference between 300D and 600D boat covers is the fabric’s weight and resulting durability. A 300D cover uses a lower denier yarn, so it’s lighter, easier to handle, and works well if you store your boat indoors or use it in mild conditions. A 600D cover doubles the fiber thickness, giving better abrasion resistance, longer wear life, and improved water resistance, often with heavier polyester and a thicker PU coating. For example, choose 300D for a small runabout you clean and store frequently; choose 600D for longer outdoor storage, trailering, or rougher climates.
Boating Enthusiasts — Join the Crew!
Free Boat Protection Guide Download Yours Now
Get your free copy of The Complete Boat Protection Guide — expert tips, real-world strategies, and exclusive insights from the Safeboatz team.

 SafeBOT
SafeBOT


